- java.lang.Object
-
- de.jstacs.utils.Normalisation
-
public class Normalisation extends Object
This class can be used for normalisation of anydoublearray or a part of adoublearray.- Author:
- Jens Keilwagen, Jan Grau
-
-
Constructor Summary
Constructors Constructor and Description Normalisation()
-
Method Summary
All Methods Static Methods Concrete Methods Modifier and Type Method and Description static doublegetLogSum(double... lnVal)Returns the logarithm of the sum of valuesval[i]given aslnVal[i] = Math.log( val[i] ).static doublegetLogSum(int start, int end, double... lnVal)Returns the logarithm of the sum of valuesv[i]given aslnVal[i] = Math.log( val[i] )between a start and end index.static doublelogSumNormalisation(double[] d)The method does a log-sum-normalisation on the arrayd, where the values ofdare assumed to be logarithmised.static doublelogSumNormalisation(double[] d, double offset)The method does a log-sum-normalisation on the arrayd, where the values ofdare assumed to be logarithmised.static doublelogSumNormalisation(double[] d, int startD, int endD)The method does a log-sum-normalisation on the values of the arraydbetween start indexstartDand end indexendD, where the values ofdare assumed to be logarithmised.static doublelogSumNormalisation(double[] d, int startD, int endD, double[] secondValues)The method does a log-sum-normalisation on the values of the arraydbetween start indexstartDand end indexendD, where the values ofdare assumed to be logarithmised.static doublelogSumNormalisation(double[] d, int startD, int endD, double[] secondValues, double[] dest, int startDest)The method does a log-sum-normalisation on the values of the arraydbetween start indexstartDand end indexendD, where the values ofdare assumed to be logarithmised.static doublelogSumNormalisation(double[] d, int startD, int endD, double[] dest, int startDest)The method does a log-sum-normalisation on the values of the arraydbetween start indexstartDand end indexendD, where the values ofdare assumed to be logarithmised.static doublelogSumNormalisation(double[] d, int startD, int endD, double offset, double[] secondValues, double[] dest, int startDest)The method does a log-sum-normalisation on the values of the arraydbetween start indexstartDand end indexendD, where the values ofdare assumed to be logarithmised.static doublelogSumNormalisation(double[] d, int startD, int endD, double offset, double[] dest, int startDest)The method does a log-sum-normalisation on the values of the arraydbetween start indexstartDand end indexendD, where the values ofdare assumed to be logarithmised.static voidnormalisation(double[] d, double v)The method does a normalisation ondusing the valuevfor normalisation.static voidnormalisation(double[] d, double v, double[] dest, int start)The method does a normalisation ondwriting the result todeststarting at positionstartwhiledremains unchanged.static voidnormalisation(double[] d, double v, int start, int end)The method does a sum normalisation ondbetween start indexstartand end indexendusing the valuevfor the normalisation.static doublesumNormalisation(double[] d)The method does a sum-normalisation ond, i.e.static doublesumNormalisation(double[] d, double[] dest, int start)The method does a sum-normalisation ond, i.e.
-
-
-
Method Detail
-
getLogSum
public static double getLogSum(double... lnVal)
Returns the logarithm of the sum of valuesval[i]given aslnVal[i] = Math.log( val[i] ).- Parameters:
lnVal- the logs of the values, i.e.lnVal[i] = Math.log( val[i] )- Returns:
- the logarithm of the sum of values
![$\log(\sum_i \mathrm{val}[i])$](images/Normalisation_LaTeXil94_1.png)
- See Also:
getLogSum(int, int, double...)
-
getLogSum
public static double getLogSum(int start, int end, double... lnVal)Returns the logarithm of the sum of valuesv[i]given aslnVal[i] = Math.log( val[i] )between a start and end index.- Parameters:
start- the first index inlnValconsidered for the sumend- the index after the last index considered for the sumlnVal- the logs of the values, i.e.lnVal[i] = Math.log( val[i] )- Returns:
- the logarithm of the sum of values between the start and end
index
![$\log(\sum_{i=start}^{end - 1} \mathrm{val}[i])$](images/Normalisation_LaTeXil95_1.png)
-
logSumNormalisation
public static double logSumNormalisation(double[] d)
The method does a log-sum-normalisation on the arrayd, where the values ofdare assumed to be logarithmised. Let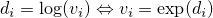 and
and 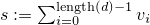 .
Then after log-sum-normalisation, the array
.
Then after log-sum-normalisation, the array dcontains the normalized original values, i.e.,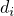 is set to
is set to
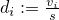 . The method returns the log-sum of the values,
. The method returns the log-sum of the values, 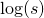 .
.- Parameters:
d- the array with the logarithmised values that should be normalised- Returns:
- the logarithm of the sum of the values
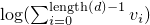
- See Also:
logSumNormalisation(double[], int, int, double[], int)
-
logSumNormalisation
public static double logSumNormalisation(double[] d, int startD, int endD)The method does a log-sum-normalisation on the values of the arraydbetween start indexstartDand end indexendD, where the values ofdare assumed to be logarithmised. Let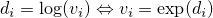 and
and 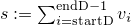 .
Then after log-sum-normalisation, the part of the array
.
Then after log-sum-normalisation, the part of the array dbetween start indexstartDand end indexendDcontains the normalized original values, i.e.,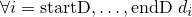 is set to
is set to
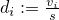 . The method returns the log-sum of the values,
. The method returns the log-sum of the values, 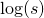 .
.- Parameters:
d- the array with the logarithms of the values that should be normalisedstartD- the first index indconsidered for the log-sum-normalisationendD- the index after the last index indconsidered for the log-sum-normalisation- Returns:
- the logarithm of the sum of the values between
startDandendD![$\log(\sum_{i=\mathrm{startD}}^{\mathrm{endD}-1} val[i])$](images/Normalisation_LaTeXil104_1.png)
- See Also:
logSumNormalisation(double[], int, int, double[], int)
-
logSumNormalisation
public static double logSumNormalisation(double[] d, int startD, int endD, double[] secondValues)The method does a log-sum-normalisation on the values of the arraydbetween start indexstartDand end indexendD, where the values ofdare assumed to be logarithmised. In addition todanother array of valuessecondValuesis considered for the normalization constant, but not normalized itself. Let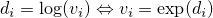 and
and 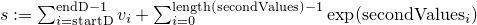 .
Then after log-sum-normalisation, the part of the array
.
Then after log-sum-normalisation, the part of the array dstarting at indexstartDcontains the normalized original values, i.e.,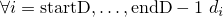 is set to
is set to
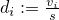 . The method returns the log-sum of the values,
. The method returns the log-sum of the values, 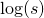 .
The method overwrites the values of
.
The method overwrites the values of dstarting at positionstartD!.secondValueswill be changed during log-sum-normalisation and will not be written tod.- Parameters:
d- the array with the logarithmised values that should be normalisedstartD- the first index indconsidered for the log-sum-normalisationendD- the index after the last index indconsidered for the log-sum-normalisationsecondValues- second array with additional values, the whole array is considered for the log-sum-normalisation- Returns:
- the logarithm of the sum of the values of
dbetweenstartDandendDand the values ofsecondValue
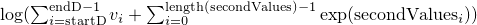
-
logSumNormalisation
public static double logSumNormalisation(double[] d, int startD, int endD, double[] dest, int startDest)The method does a log-sum-normalisation on the values of the arraydbetween start indexstartDand end indexendD, where the values ofdare assumed to be logarithmised. Let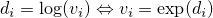 and
and 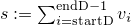 .
Then after log-sum-normalisation, the part of the array
.
Then after log-sum-normalisation, the part of the array deststarting at indexstartDestcontains the normalized original values, i.e.,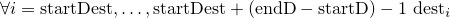 is set to
is set to
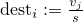 where
where 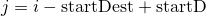 . The method returns the log-sum of the values,
. The method returns the log-sum of the values, 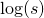 .
The method writes the result of
.
The method writes the result of dindeststarting at positionstartDestwhiledremains unchanged.secondValueswill be changed during log-sum-normalisation and will not be written todest.- Parameters:
d- the array with the logarithmised values that should be normalisedstartD- the first index indconsidered for the log-sum-normalisationendD- the index after the last index indconsidered for the log-sum-normalisationdest- the destination array for the normalised valuesstartDest- the start index of the destination array- Returns:
- the logarithm of the sum of the values of
dbetweenstartDandendD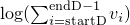
-
logSumNormalisation
public static double logSumNormalisation(double[] d, int startD, int endD, double[] secondValues, double[] dest, int startDest)The method does a log-sum-normalisation on the values of the arraydbetween start indexstartDand end indexendD, where the values ofdare assumed to be logarithmised. In addition todanother array of valuessecondValuesis considered for the normalization constant, but not normalized itself. Let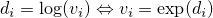 and
and 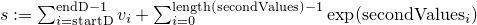 .
Then after log-sum-normalisation, the part of the array
.
Then after log-sum-normalisation, the part of the array deststarting at indexstartDestcontains the normalized original values, i.e.,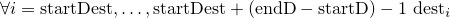 is set to
is set to
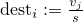 where
where 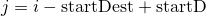 . The method returns the log-sum of the values,
. The method returns the log-sum of the values, 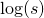 .
The method writes the result of
.
The method writes the result of dindeststarting at positionstartDestwhiledremains unchanged.secondValueswill be changed during log-sum-normalisation and will not be written todest.- Parameters:
d- the array with the logarithmised values that should be normalisedstartD- the first index indconsidered for the log-sum-normalisationendD- the index after the last index indconsidered for the log-sum-normalisationsecondValues- second array with additional values, the whole array is considered for the log-sum-normalisationdest- the destination array for the normalised valuesstartDest- the start index of the destination array- Returns:
- the logarithm of the sum of the values of
dbetweenstartDandendDand the values ofsecondValue
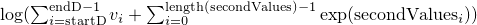
-
logSumNormalisation
public static double logSumNormalisation(double[] d, double offset)The method does a log-sum-normalisation on the arrayd, where the values ofdare assumed to be logarithmised. Let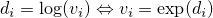 and
and 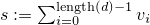 .
Then after log-sum-normalisation, the array
.
Then after log-sum-normalisation, the array dcontains the normalized original values, i.e.,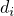 is set to
is set to
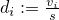 . The method returns the log-sum of the values,
. The method returns the log-sum of the values, 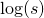 .
.- Parameters:
d- the array with the logarithmised values that should be normalisedoffset- the offset on the log-values which is used to get more accurate results in the normalization. Typically, this is set to the maximum of the log-values.- Returns:
- the logarithm of the sum of the values
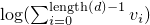
- See Also:
logSumNormalisation(double[], int, int, double[], int)
-
logSumNormalisation
public static double logSumNormalisation(double[] d, int startD, int endD, double offset, double[] dest, int startDest)The method does a log-sum-normalisation on the values of the arraydbetween start indexstartDand end indexendD, where the values ofdare assumed to be logarithmised. Let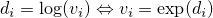 and
and 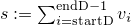 .
Then after log-sum-normalisation, the part of the array
.
Then after log-sum-normalisation, the part of the array deststarting at indexstartDestcontains the normalized original values, i.e.,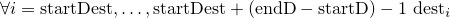 is set to
is set to
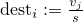 where
where 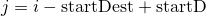 . The method returns the log-sum of the values,
. The method returns the log-sum of the values, 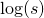 .
The method writes the result of
.
The method writes the result of dindeststarting at positionstartDestwhiledremains unchanged.secondValueswill be changed during log-sum-normalisation and will not be written todest.- Parameters:
d- the array with the logarithmised values that should be normalisedstartD- the first index indconsidered for the log-sum-normalisationendD- the index after the last index indconsidered for the log-sum-normalisationoffset- the offset on the log-values which is used to get more accurate results in the normalization. Typically, this is set to the maximum of the log-values.dest- the destination array for the normalised valuesstartDest- the start index of the destination array- Returns:
- the logarithm of the sum of the values of
dbetweenstartDandendD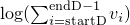
-
logSumNormalisation
public static double logSumNormalisation(double[] d, int startD, int endD, double offset, double[] secondValues, double[] dest, int startDest)The method does a log-sum-normalisation on the values of the arraydbetween start indexstartDand end indexendD, where the values ofdare assumed to be logarithmised. In addition todanother array of valuessecondValuesis considered for the normalization constant, but not normalized itself. Let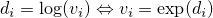 and
and 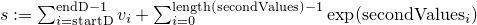 .
Then after log-sum-normalisation, the part of the array
.
Then after log-sum-normalisation, the part of the array deststarting at indexstartDestcontains the normalized original values, i.e.,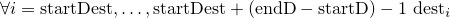 is set to
is set to
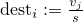 where
where 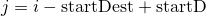 . The method returns the log-sum of the values,
. The method returns the log-sum of the values, 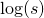 .
The method writes the result of
.
The method writes the result of dindeststarting at positionstartDestwhiledremains unchanged.secondValueswill be changed during log-sum-normalisation and will not be written todest.- Parameters:
d- the array with the logarithmised values that should be normalisedstartD- the first index indconsidered for the log-sum-normalisationendD- the index after the last index indconsidered for the log-sum-normalisationoffset- the offset on the log-values which is used to get more accurate results in the normalization. Typically, this is set to the maximum of the log-values.secondValues- second array with additional values, the whole array is considered for the log-sum-normalisationdest- the destination array for the normalised valuesstartDest- the start index of the destination array- Returns:
- the logarithm of the sum of the values of
dbetweenstartDandendDand the values ofsecondValue
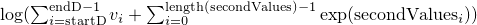
-
sumNormalisation
public static double sumNormalisation(double[] d)
The method does a sum-normalisation ond, i.e. divides all values indby the sum over all values indand returns the sum of the values.- Parameters:
d- the array with the values that should be normalised- Returns:
- the sum of the values of
d![$\sum_{i=0}^{\mathrm{length}(d)-1} d[i]$](images/Normalisation_LaTeXil112_1.png)
- See Also:
sumNormalisation(double[], double[], int)
-
sumNormalisation
public static double sumNormalisation(double[] d, double[] dest, int start)The method does a sum-normalisation ond, i.e. divides all values indby the sum over all values indand writes the result todeststarting at positionstartwhiledremains unchanged. The sum of the values ofdwill be returned.- Parameters:
d- the array with the values that should be normaliseddest- the destination array for the normalised valuesstart- the start index of the destination array- Returns:
- the sum of the values of
d![$\sum_{i=0}^{\mathrm{length}(d)-1} d[i] $](images/Normalisation_LaTeXil113_1.png)
-
normalisation
public static void normalisation(double[] d, double v)The method does a normalisation ondusing the valuevfor normalisation.- Parameters:
d- the array with the values that should be normalisedv- the value for the normalisation- See Also:
normalisation(double[], double, double[], int)
-
normalisation
public static void normalisation(double[] d, double v, double[] dest, int start)The method does a normalisation ondwriting the result todeststarting at positionstartwhiledremains unchanged. The valuevis used for the normalisation.- Parameters:
d- the array with the values that should be normalisedv- the value for normalisationdest- the destination array for the normalised valuesstart- the start index of the destination array
-
normalisation
public static void normalisation(double[] d, double v, int start, int end)The method does a sum normalisation ondbetween start indexstartand end indexendusing the valuevfor the normalisation.- Parameters:
d- the array with the values that should be normalisedv- the value for normalisationstart- the first index indconsidered for the log-sum-normalisationend- the index after the last index indconsidered for the log-sum-normalisation
-
-